Understanding Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS): Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) is a chronic pain condition that affects the muscles and their surrounding fascia. This disorder typically manifests as persistent pain in specific areas or radiates to other parts of the body. Common causes include stress, poor posture, and overuse of muscles. If left untreated, MPS can lead to discomfort and reduced quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of MPS, including its causes, symptoms, dietary recommendations, and exercises that can help alleviate discomfort.
What is Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS)?
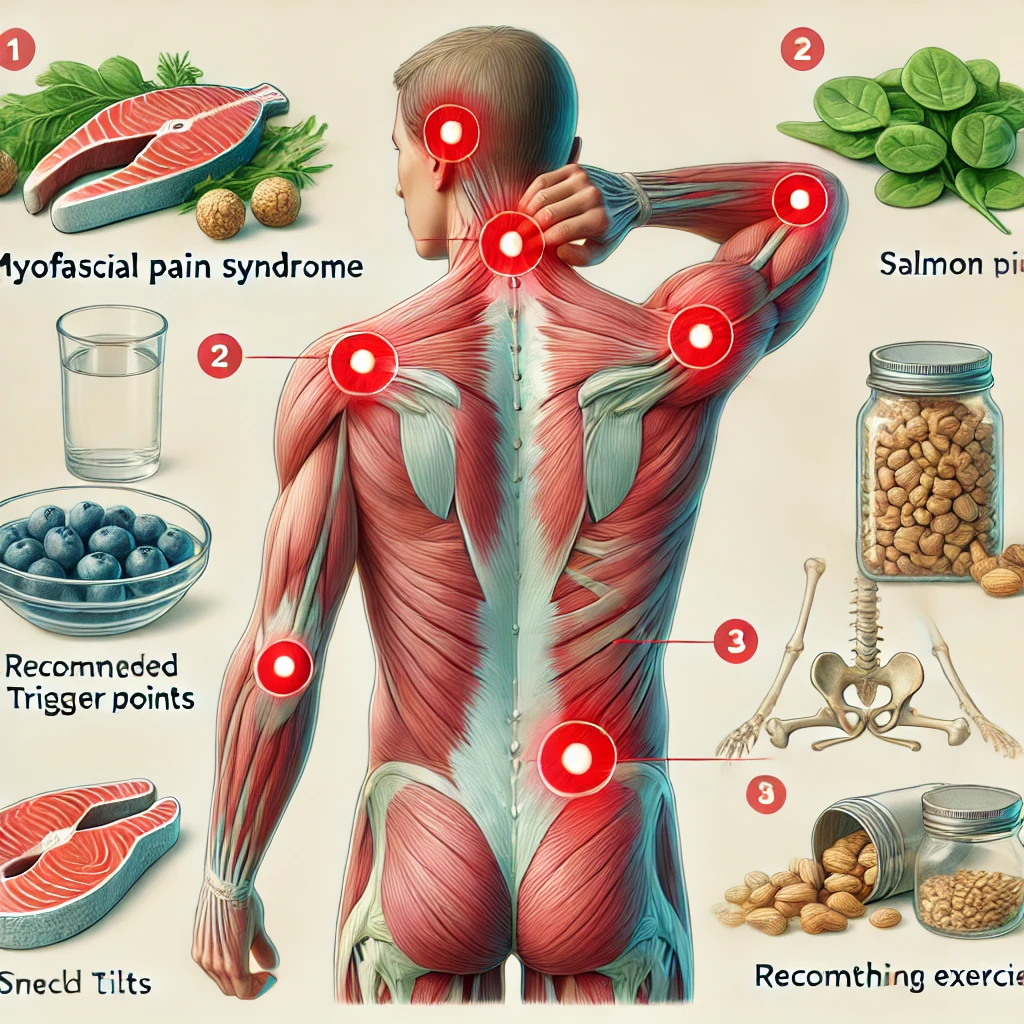
Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) is characterized by pain in the fascia, the connective tissue that surrounds muscles. This condition typically arises when a trigger point (a sensitive area within the muscle) becomes irritated, causing localized pain or referred pain in other regions of the body. Trigger points are often the result of muscle strain, poor posture, or prolonged inactivity, making MPS a common issue for many people, especially those with desk jobs or sedentary lifestyles.
The pain from MPS can be sharp or aching and tends to worsen with movement or pressure on the affected muscle. The most commonly affected areas are the neck, shoulders, and lower back. In some cases, individuals may also experience headaches or limited range of motion due to muscle stiffness. It is important to recognize the symptoms early on, as untreated MPS can result in chronic discomfort and even muscle atrophy.
Causes of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
The primary causes of MPS are:
- Muscle Overuse 💪: Repetitive strain on muscles, especially those that are not given adequate time to rest and recover, can lead to the formation of trigger points.
- Poor Posture 🧑💻: Sitting or standing in incorrect postures for extended periods can stress certain muscle groups, leading to tension and the development of trigger points.
- Stress and Anxiety 😰: Emotional stress can result in muscle tightness, particularly in areas like the neck and shoulders, exacerbating the risk of MPS.
- Injury or Trauma 🚑: Physical injuries, such as sprains or strains, can create lasting muscle pain if not properly treated.
- Sedentary Lifestyle 🛋️: Lack of physical activity can lead to muscle weakness and tightness, increasing the likelihood of MPS.
Symptoms of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
The hallmark of MPS is the presence of trigger points, which are small, tight knots in the muscles that cause pain when pressed. Common symptoms include:
- Localized Muscle Pain 🩹: Typically in the neck, shoulders, or lower back, the pain may feel deep and persistent.
- Referred Pain 🌐: The pain from a trigger point can radiate to other areas of the body, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact cause of the discomfort.
- Stiffness and Limited Mobility 🤕: People with MPS often experience difficulty in moving certain muscles, leading to a feeling of stiffness or tightness.
- Tension Headaches 🧠: Trigger points in the neck or upper back can lead to tension headaches, further intensifying discomfort.
Foods to Alleviate Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in the management of Myofascial Pain Syndrome. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods and nutrients that support muscle recovery can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with MPS.
Recommended Foods 🍽️:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids 🐟: Found in foods like salmon, tuna, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce muscle inflammation.
- Magnesium-Rich Foods 🍌: Magnesium is essential for muscle relaxation and can help alleviate muscle cramps and spasms. Include foods such as bananas, spinach, and nuts in your diet.
- Protein-Rich Foods 🍗: Protein is essential for muscle repair and recovery. Foods like chicken breast, eggs, and legumes can promote muscle healing.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods 🫐: Blueberries, tomatoes, and green tea are high in antioxidants that help protect muscles from damage caused by free radicals.
Foods to Avoid 🚫:
- Processed Carbohydrates 🍞: Foods such as bread, pastries, and snacks made with refined flour can promote inflammation in the body, worsening MPS symptoms.
- Excessive Caffeine ☕: Too much caffeine can lead to muscle tension and exacerbate pain, especially in the neck and shoulders.
- Processed Meats 🌭: Items like sausages, bacon, and ham contain preservatives that can trigger an inflammatory response in the body, aggravating MPS.
Exercises to Relieve Myofascial Pain Syndrome
A balanced exercise routine that includes stretching and strengthening exercises can be highly effective in managing MPS. Stretching helps improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness, while strength training enhances muscle endurance and stability.
Recommended Stretching Exercises 🧘♂️:
- Neck Stretch: Tilt your head gently to one side, bringing your ear toward your shoulder, and hold for 30 seconds. Repeat on the other side. This stretches the neck muscles and can alleviate stiffness.
- Shoulder Stretch: Extend one arm across your body, using the opposite arm to pull it closer to your chest. Hold for 30 seconds and switch sides. This targets the shoulders and upper back.
- Cat-Cow Stretch: Get on your hands and knees, then alternate between arching your back (cat pose) and dropping your belly toward the floor (cow pose). This stretch is great for the lower back.
Recommended Strengthening Exercises 💪:
- Band Row: Using a resistance band, pull the band towards you while squeezing your shoulder blades together. This strengthens the muscles in the upper back.
- Plank: Hold a plank position to stabilize your core and improve overall strength and posture.
- Dumbbell Lifts 🏋️♀️: Light dumbbell exercises like shoulder presses or lateral raises can help strengthen the upper body and prevent muscle imbalances.
Conclusion ✅
Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) is a common condition that can lead to significant discomfort, affecting a person’s mobility and quality of life. The primary causes include muscle overuse, poor posture, and stress. While MPS may feel debilitating at times, it can be effectively managed through a combination of proper nutrition, stretching, and strength exercises. Maintaining a healthy diet that supports muscle recovery, coupled with regular physical activity, can go a long way in reducing pain and improving overall health.
For those suffering from MPS, it’s crucial to take a holistic approach to treatment. By addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition, individuals can enjoy a more active, pain-free life. If symptoms persist, seeking professional guidance from a healthcare provider or physical therapist is highly recommended for personalized treatment and care.
